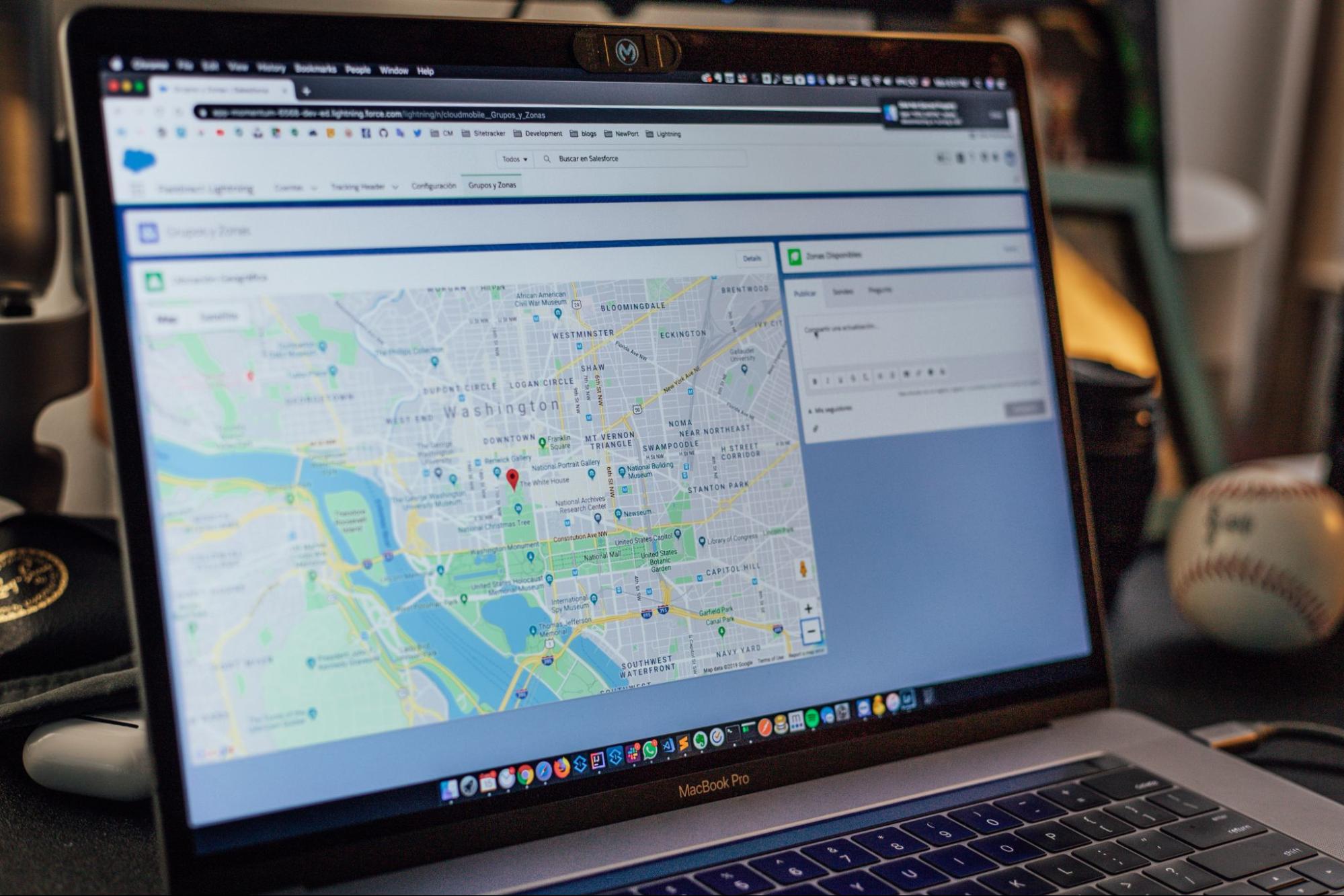
In the past, fleet managers had to utilize pen and paper to plan routes for the many vehicles used to deliver things to consumers’ doorsteps. Those days are long gone. In this digital age, automating operations and processes has become a need to fulfill the rising demands of consumers while simultaneously reducing reliance on human specialists.
In the case of route planning and optimization, the same principle applies. A vital service provider for millions of people, the logistics sector has been operating for many decades and is a long-standing business. However, the industry has only witnessed a major expansion in the last decade or two, mostly owing to technical improvement.
It is hard to envision the logistics sector running today without using technology such as route optimization applications like Route4Me, speed sensors, driver monitoring systems, real-time data transfer, predictive analysis, and a variety of other characteristics.
Like any other technological breakthrough, automation in the logistics industry has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The qualities that assist one party may be a threat to another. The same instrument can be either a strong asset or a lethal weapon depending on how it is used or misused by different individuals.
However, just like with any other digital breakthrough, there are always pros and downsides to being considered. Take a look at the two sides of the coin regarding automated fleet routing systems in this article.
Table of Contents
Pro #1: Planned routes that change dynamically
Source: descartes.com
To provide effective planning, any program must be able to develop dynamic routes if a consumer cancels their order or changes their delivery time or address while the package is on its way to the carrier. Drivers are not required to make an effort to deliver an order that has been postponed by the client while using dynamic route planning.
They get an alert as soon as the modifications are made, and the program shows a new route within a few minutes of receiving the notice. The use of dynamic route planning to automate route planning may save a significant amount of money and time.
Furthermore, it has the potential to lower the rate of “return to origin” since it enhances the likelihood of first-attempt delivery.
Pro #2: Enhanced Precision and Effectiveness
By automating repetitive or standardized operations, an organization’s total efficiency is increased by as much as 30%. Each day at a logistics firm, the data collected from cars and drivers may amount to terabytes of numbers and figures, which would take an entire day for an average person to go through.
On the other hand, computer software can make correct sense of data and analyze it in a short period. Because of the power of automation, it is feasible to monitor every vehicle and driver uniquely from the moment fleet managers acquire a new fleet and record their information (such as vehicle number, model, and so on) into a centralized database.
Using only a few button pushes, you can find out which truck is transporting which item to which location and how long it will take for the vehicle to arrive.
Pro #3: Increased number of deliveries per vehicle

Source: linkedin.com
By providing routes with no or little congestion, automated route planning increases the number of DPV (delivery points per vehicle) delivered. The engine does not have to idle as often as it would if the car were stalled in traffic, saving fuel costs.
Route planning with sophisticated transport management software, in addition to this, makes it simple to monitor all of the trucks, ensuring that they return at the scheduled time and are prepared for the next delivery.
Pro #4: Transportation Safety and Reliability are two important considerations
With real-time location tracking, both the fleet supervisor and the client know the truck’s precise position and when it is anticipated to arrive at the delivery site. Customers may trust the shipment’s arrival since they know they can check its progress at any moment using the tracking information. Other safety features, like driver monitoring systems and collision detectors, are included in the automation process.
To detect strange behavior such as intoxication or exhaustion, a camera on the steering column continually scans the driver’s eyes and notifies them and the supervisor. According to Tampa car and truck accident attorneys, the excessive size of trucks makes accidents far more deadly, with those in automobiles being the vast majority of those killed in truck accidents.
Crash detectors alert the driver if any other cars are within a certain distance, allowing them to avoid a collision if necessary. If an accident does occur, the dash cameras mounted in vehicles record the event so that the management may review the tape afterward and determine what went wrong with the trucking company.
Con #1: Job losses are a fact of life

Source: forbes.com
From a fleet manager’s perspective, the use of automation and digital devices may significantly minimize the amount of human labor required to do the same tasks. From automated data transfer to predictive maintenance analysis, software technologies are taking over tasks formerly performed by human beings.
Workers risk losing their employment to robots or computers if technological growth continues at the current pace. This issue may get complicated, mainly if labor unions and strikes are involved.
Con #2: Initial Investment Is Exorbitant
Automating processes will save your organization money in the long term and result in a favorable return on investment. However, the initial expenditure in procuring and installing all of the gadgets and educating the drivers and crew members on how to use them effectively is fairly significant and requires a significant amount of time.
When you are a manager, you should be patient enough to wait and observe how successfully your team adjusts to the new system so that you can reap the benefits later. Do not invest in telematics systems or artificial intelligence technologies until you know that your organization needs them.
Con #3: Over-reliance on machines is a problem
Source: hrmonline.com.au
People make a typical mistake regarding technology because they assume that computers and software can handle everything on their own, which is incorrect. It is always necessary to have human interaction and oversight to guarantee that software tools perform their functions appropriately.
When an automobile is engaged in an accident, sensors attached to the vehicle continuously convey data and sound an alarm. At that point, you should assume control and determine how to proceed with the delivery and what should be done to ensure the driver’s well-being and other considerations. It is not always possible to rely on a machine to complete a whole process independently.
Automation for fleet management is unquestionably a strong tool, but it also has a negative side effect that must be considered. You must learn to utilize your authority wisely to reap the most possible advantage for yourself, your employees, the business, and the customer.
As a result of being aware of the advantages and disadvantages, you can make an educated choice about modernizing your fleet with the newest equipment and automation technologies.







