Gynecology concerns issues and diseases have to do with female genitalia including the labia, vaginal canal, cervix, uterus, and ovaries. Gynecological medicine can be both preventive and surgical. Issues and diseases may be sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes simplex virus, cancerous such as ovarian and vaginal, traumatic such as tears, lacerations, and bruising, and a host of other issues.
Patients with gynecological issues may initially visit their GP before being referred to a gynecological specialist. Broadly, gynecological conditions can fall under several categories.
Table of Contents
General Gynaecological Issues
- Acne and Abnormal Female Hair Distribution
- Endometriosis
- Genital Tract Infections
- Irregular Bleeding
- Ovarian Cysts
- Pelvic Pain
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
- Uterine Fibroids
- Vulva and Vagina Skin Disorders
Contraception/Abortion
Infertility
Menopause
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Osteoporosis Prevention
- Post-Menopausal Bleeding
Pelvic Floor Disorders
- Pelvic prolapse
- Urinary Incontinence
- Urinary Tract Infection
Common problems are uterine bleeding, chlamydia, decreased libido, infertility, vaginitis, ovarian cysts, etc. According to data, the four most common presentations for which patients visit their GP or gynecologist are endometriosis, irregular bleeding, uterine fibroids, and yeast infections.
Presentations Most Commonly Seen by Gynaecologists

img source: gynaemd.com.sg
The following four presentations or conditions are the ones most commonly brought to the attention of physicians and gynecologists. Please keep in mind that many conditions, such as STDs, maybe go unnoticed by the patient or may come with the social stigma that makes it difficult for patients to seek medical care.
Endometriosis
At the end of the menstrual cycle, the uterus discharges menstrual fluid also known as the endometrium. This is normal. However, sometimes this endometrial tissue grows on the outside of the uterus, causing scars that may turn into lesions or growths. Today, most doctors will prescribe pain medication unless symptoms are severe. In which case, surgery may be necessary.
Irregular Bleeding
This is one of the most common issues patients may bring to their gynecologist. For most women, the menstrual period lasts five days, including one day of heavy bleeding and several lighter days. During this period, women will also experience some clotting and cramping. However, if the heavy bleeding, clotting, and cramping continue for more than a few days, it is recommended that the patient contact their doctor. Treatment for irregular bleeding may include prescription drugs or surgery for more serious cases.
Uterine Fibroids
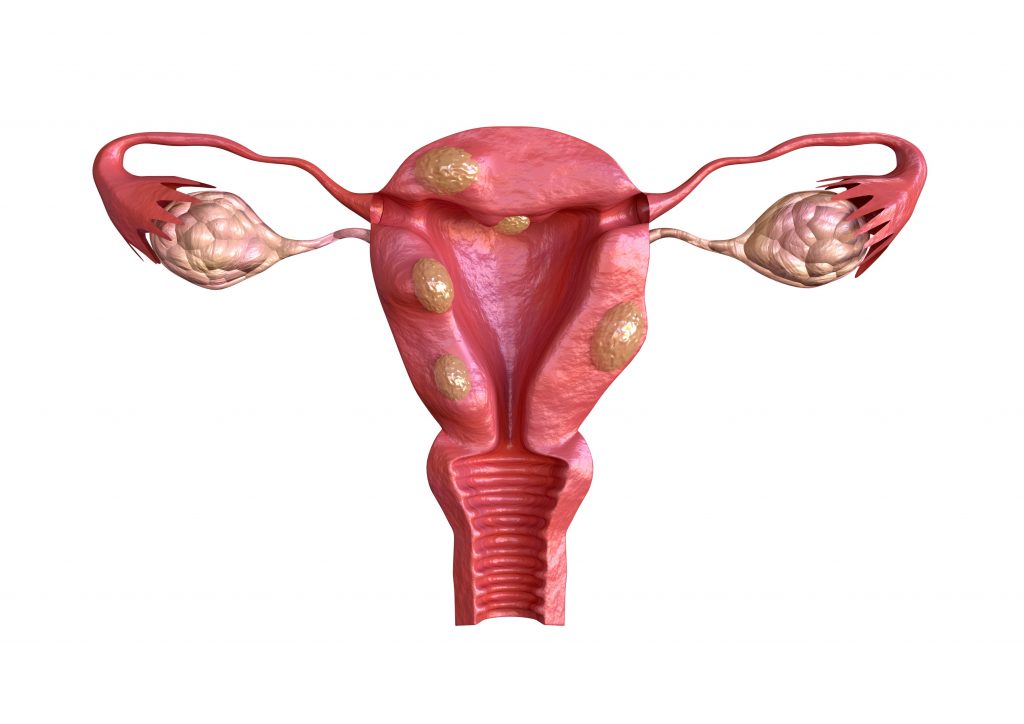
img source: medium.com
Another issue common to the uterus is the formation of fibroids or nodules within the wall of the uterus. These fibroids are not cancerous, but they can be painful and may cause excessive bleeding during the menstruation period. In the past, hysterectomy or the removal of the uterus was the only treatment. But recently, anti-inflammatory medication may be enough to treat the issue.
Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are common, with three out of four women experiencing them at least once during their lifetime. A yeast infection is an overgrowth of the yeast that normally lives in the vagina, causing vaginal irritation. Pregnancy, diabetes, the use of feminine hygiene products such as douches, certain contraceptives, tight or poorly ventilated clothing, etc. are common causes of infection. Treatment is usually medicinal.
Other Common Issues and Cases
img source: vectorstock.com
Beyond the above-mentioned issues, patients may visit the gynecologist for a host of issues. Broadly, these fall under the areas or categories of direct physical injury to the genitalia, diseases received during a sexual transaction, and various cancers.
Physical Injury
Various physical injuries or trauma to the genital area is another common reason to visit the gynecologist. Blunt force trauma to exposed areas such as the vulva during physical activity such as cycling may cause extreme swelling or laceration. In most cases, minor procedures such as stitching, or a period of recuperation and less activity will suffice as treatment.
Sexually Transmitted Disease
The most common sexually transmitted disease (STD) in women is the human papillomavirus or HPV. There are over 100 types of HPV and it can be passed on through genital contact and the mouth. In many cases, HPV will not show symptoms. However, HPV can cause genital warts and lead to cancer of the cervix, along with anus and throat.
Other common STDs are gonorrhea, chlamydia, and genital herpes. Gonorrhea is bacteria-based, and its symptoms include an increased need to urinate, discharge from the vagina, heavier periods, pain during sexual intercourse, burning feeling during urination, abdominal pain, fever, and sore throat.
Chlamydia is also bacteria-based. It presents no symptoms in 90 percent of women but may cause serious problems later if left untreated, including inflammation of the urethra.
Like HPV, genital herpes is viral and affects 1 in 6 women. Herpes causes herpetic sores which are painful bumps full of fluid. Unfortunately, pregnant women with herpes may pass it on to the baby during vaginal delivery. This can lead to blindness, brain damage, and possibly death of the baby. This risk is not common, however.
Cancer
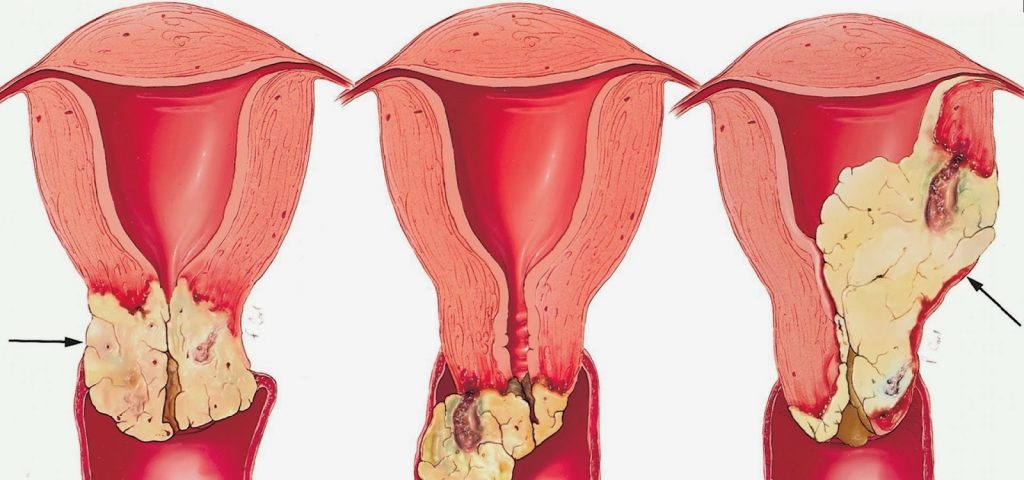
img source: blogspot.com
There are five gynecological cancers including cervical, ovarian, vaginal, vulval, and womb. The symptoms of each are as follows:
Cervical
– Bleeding after sex
– Pain during sex
– Smelly vaginal discharge
Ovarian
– Bloating
– Pelvic and/or abdominal pain
– Nausea
– Irregular bowel moment
– Frequent urination
Vaginal

img source: rbl.ms
– Bleeding after sex
– Pain during sex
– Smelly vaginal discharge
– Vaginal lumps
– Vaginal itch
Vulval
– Persistent itch
– Pain
– Thickened, irritated patches on the vulva
– Lump on vulva
Womb
– Bleeding after sex
– Heavy periods
– Vaginal discharge
When to See a Gynaecologist

img source: momnewsdaily.com
It is recommended that women visit a gynecologist not only when symptoms such as pain or unusual bleeding occur, but also regularly to catch problems early. The current recommendation for check-ups for a healthy woman is once a year. Check-up procedures include a visual inspection by the doctor and screening tests such as pap smear for cancer or swipe and blood tests for STDs. Gynecologists also address and treat issues and concerns such as contraception, fertility, and abortion. Patients may first visit a GP and receive a referral to a larger hospital with a gynecological department or to a private practice specialist gynecologist. Dr Vivek Arora is a Specialist Gynaecologist based in Sydney.