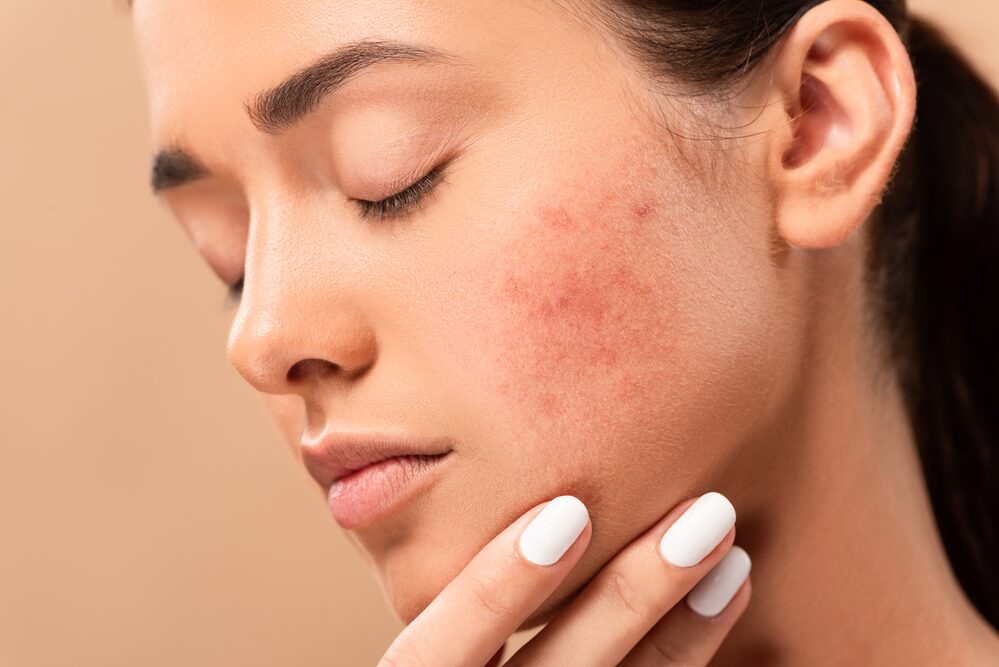
The link between diet and acne, particularly hormonal acne, is a topic that has garnered increasing attention in the realms of dermatology and nutrition. Hormonal acne, which typically manifests along the jawline and chin, is often influenced by fluctuations in hormones such as androgens and insulin. These hormonal changes can lead to increased oil production, clogged pores, and inflammation, which are prime conditions for acne development. Diet plays a crucial role in this scenario, as certain foods and eating patterns can either exacerbate or mitigate these hormonal fluctuations. Understanding how different dietary elements impact skin health and hormonal balance is the first step in managing hormonal acne effectively through nutrition.
Hormonal fluctuations are a primary factor in the development of acne, especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Androgens, for instance, can increase sebum production and lead to clogged pores. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) also play a significant role; diets high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can spike insulin levels, further exacerbating acne. These hormonal imbalances can be influenced by diet, making it a critical aspect of managing and reducing hormonal acne. By understanding these connections, individuals can make informed dietary choices that may help in balancing hormone levels and reducing acne flare-ups.
Table of Contents
Foods That Influence Hormonal Acne
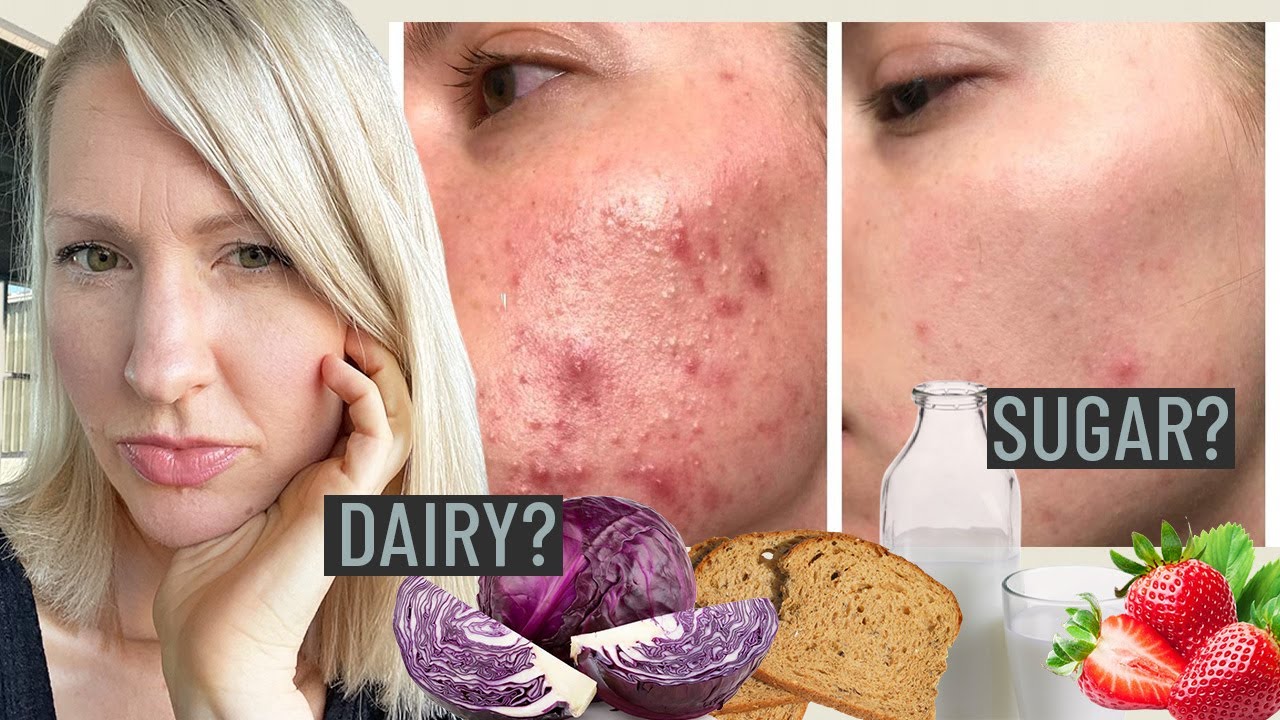
Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) are known to cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. This spike in insulin can increase the production of androgens, which in turn stimulates sebum production and exacerbates acne. Common high-GI foods include white bread, sugary cereals, pastries, and other refined carbohydrates. Reducing the intake of these foods and opting for lower-GI alternatives can help in regulating hormone levels and potentially reducing acne severity.
Dairy products, particularly skim milk, have been linked to acne development in several studies. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it’s believed that hormones and bioactive molecules in dairy can influence insulin levels and androgen activity, thus contributing to acne. While not everyone is sensitive to dairy, those with hormonal acne might benefit from reducing their dairy intake or choosing dairy alternatives to see if there is an improvement in their skin condition.
The type of fats consumed can significantly impact hormonal acne. Saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, baked goods, and certain meats can promote inflammation, a key factor in acne development. Conversely, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can have anti-inflammatory effects and may help in reducing acne severity. Understanding the different types of fats and their impact on skin health is essential for individuals looking to manage their hormonal acne through diet.
Dietary Recommendations for Hormonal Acne

Source: drbrighten.com
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in managing hormonal acne. This involves a variety of nutrients that support hormonal balance and skin health. Such a diet includes ample vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. It’s not just about eliminating harmful foods but also about incorporating those that promote overall health. A balanced diet helps in stabilizing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and providing essential nutrients that aid in skin repair and maintenance.
Low-glycemic carbohydrates are a key component of an acne-reducing diet plan. These carbs, which include whole grains, legumes, and most fruits and vegetables, release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing the insulin spikes that can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and acne. Incorporating these foods into meals not only helps in managing acne but also supports overall health by providing essential nutrients and fiber.
Lean proteins, such as chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes, are important for skin health as they provide the building blocks for skin repair and can help in balancing hormone levels. Healthy fats, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids like those found in fish, nuts, and seeds, can reduce inflammation in the body, including skin inflammation associated with acne. These dietary elements are essential for a holistic approach to managing hormonal acne.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods and Antioxidants
Fruits and vegetables are loaded with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that can help combat inflammation and oxidative stress – two factors that contribute to acne development. Brightly colored fruits and vegetables, such as berries, carrots, and leafy greens, are particularly high in these beneficial compounds. Regular consumption of a variety of fruits and vegetables can support skin health and reduce acne flare-ups.
Nuts and seeds are not only great sources of healthy fats but also contain vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support skin health. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, for instance, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and vitamin E, all of which have been linked to improved skin health and reduced acne.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet is a crucial strategy in managing hormonal acne. This includes not only fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds but also spices like turmeric and ginger, and fatty fish like salmon. These foods can help reduce the inflammation associated with acne and support overall skin health.
Hydration and Supplements in Acne Management
Source: abbeyskitchen.com
Hydration is a fundamental aspect of skin health and acne management. Adequate water intake ensures that the skin remains hydrated, which is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing dryness and irritation. Water also helps in flushing out toxins and can aid in reducing the buildup of substances that can clog pores and lead to acne. Encouraging a consistent intake of water throughout the day is a simple yet effective strategy for enhancing skin health and managing acne.
Supplements can play a supportive role in managing hormonal acne. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil supplements, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can be beneficial in reducing the inflammation associated with acne. Zinc is another supplement that has been linked to improved acne symptoms. It helps in wound healing, reduces inflammation, and has been shown to inhibit the growth of acne-causing bacteria. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, especially for individuals with specific health conditions or those taking other medications.
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help balance the gut microbiome, and this balance has been linked to skin health. A healthy gut can reduce inflammation throughout the body, including the skin, and may help in managing acne. Probiotics can be consumed through fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha, or through supplements. While research is still evolving in this area, incorporating probiotics into the diet may be a beneficial strategy for those dealing with hormonal acne.
Debunking Myths and Personalizing Diet
There are many myths surrounding diet and acne, and it’s crucial to address these misconceptions. For instance, the belief that oily foods directly cause acne is oversimplified and not supported by scientific evidence. While diet can influence skin health, acne is a complex condition with various contributing factors. Another common myth is that chocolate directly causes acne; while excessive sugar intake can exacerbate acne, chocolate itself is not a direct cause. Debunking these myths is important for understanding the true relationship between diet and acne.
Dietary responses and skin reactions can vary greatly from person to person. What might trigger acne in one individual may not have the same effect in another. This variability underscores the importance of personalizing dietary approaches to acne management. Observing how one’s skin reacts to certain foods and adjusting the diet accordingly is a practical strategy. Keeping a food diary can be a helpful tool in identifying potential triggers and making informed dietary changes.
Creating a tailored diet plan for acne management involves taking into account individual dietary preferences, lifestyle, and any specific sensitivities or allergies. It’s not about strict dietary restrictions but finding a balance that works for the individual while focusing on nutrient-rich foods that support skin health. Consulting with a
or dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and ensure that dietary changes align with overall health goals.
Holistic Approach to Hormonal Acne

Source: isabellasclearly.com
Managing hormonal acne effectively requires a holistic approach that goes beyond dietary changes. While nutrition plays a crucial role, it’s important to integrate other strategies for comprehensive acne management. This includes proper skincare routines, stress management, and, in some cases, medical treatments like topical retinoids or hormonal therapies. Lifestyle factors such as sleep quality and physical activity also have an impact on skin health. Addressing acne from multiple angles increases the likelihood of improving skin condition and maintaining long-term results.
It’s vital to remember that while dietary changes can significantly impact acne, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. Severe cases of hormonal acne often require a combination of dietary adjustments and medical treatments. Consulting with healthcare professionals like dermatologists and nutritionists ensures that individuals receive tailored advice and treatments that are safe and effective. They can help in identifying the underlying causes of acne, suggest appropriate dietary changes, and recommend suitable medical treatments if necessary.
Managing hormonal acne through dietary changes involves understanding the connection between diet and skin health, identifying foods that may trigger or reduce acne, and incorporating a balanced diet rich in low-glycemic carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It’s also important to consider the role of hydration, supplements, and probiotics.
Debunking common myths and tailoring the diet to individual needs are essential for effective acne management. However, a holistic approach that combines diet with other lifestyle and medical strategies, guided by professional advice, is crucial for achieving the best results. Remember, each person’s skin is unique, and what works for one may not work for another; patience and persistence are key in the journey towards clearer skin.