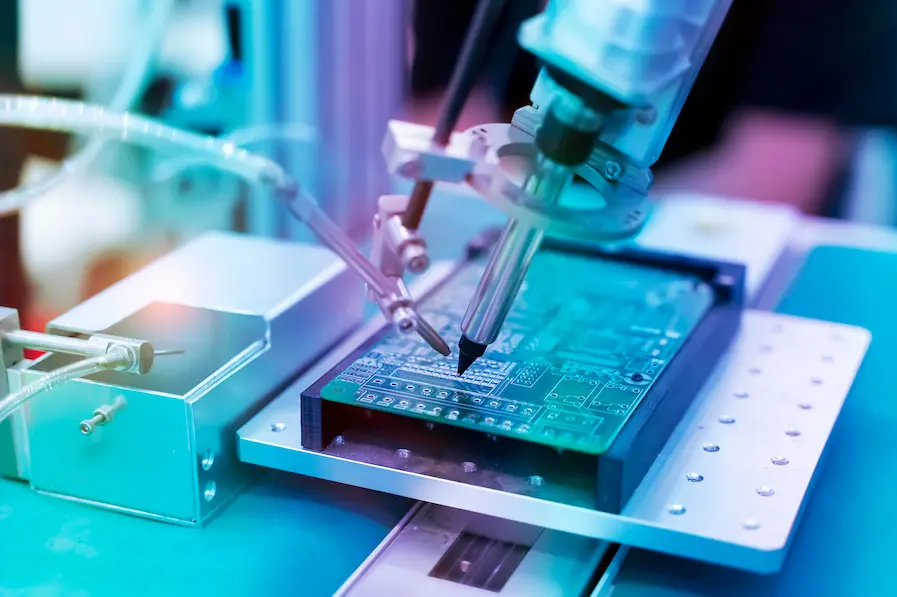

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the electronics industry, streamlining manufacturing processes and enabling the production of complex electronic components with unparalleled precision. This technology has found widespread applications across various stages of electronics production, from circuit board designs to antenna arrays. In this blog post, we’ll explore 10 fascinating ways CNC machining is used in the electronics industry, uncovering its essential role in enhancing efficiency, quality, and innovation.
Table of Contents
1. CNC’s Role in Producing Intricate Circuit Board Designs
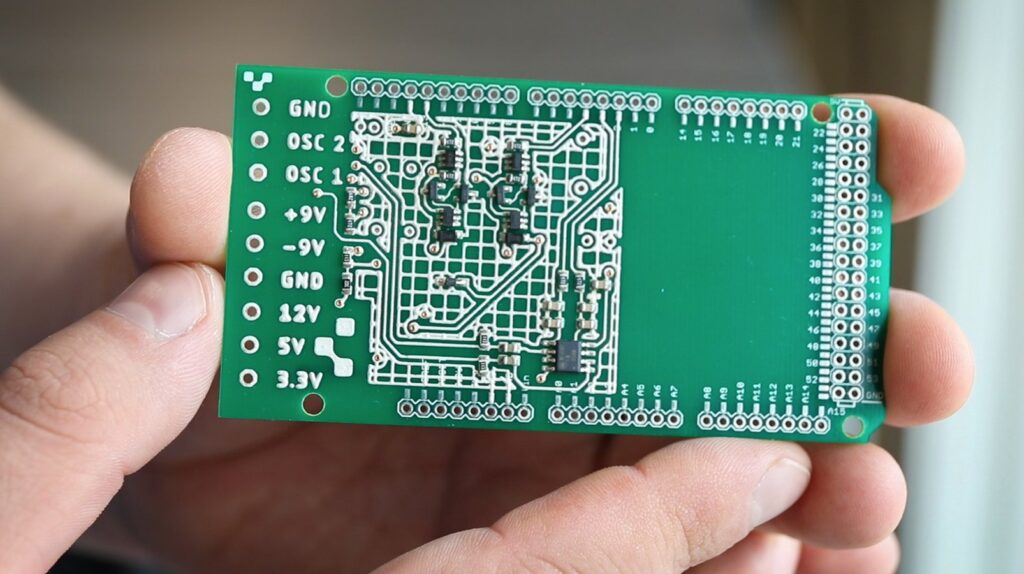
Source: all3dp.com
CNC machining plays a crucial role in producing intricate circuit board designs. With its computer-controlled precision, these routers, and mills can etch complex patterns onto circuit board substrates with unparalleled accuracy. This level of detail ensures optimal signal flow and reduced interference, leading to more reliable and efficient electronic devices. By eliminating human error and offering the ability to work with microscopic dimensions, technology enables the creation of miniaturized circuit boards that push the boundaries of electronics manufacturing. Its ability to handle intricate designs and complex geometries makes CNC an indispensable tool in the quest for cutting-edge electronic advancements.
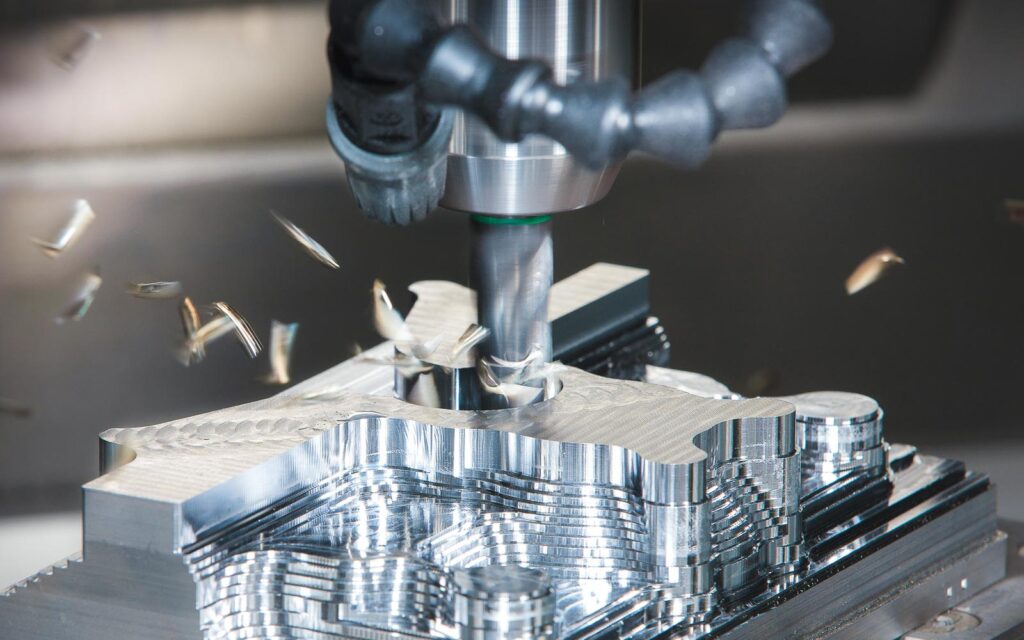
2. Precision Drilling and Milling for Electronic Components
Electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and microchips, require precise drilling and milling to function optimally. This is where a CNC machine shop excels, providing manufacturers with the ability to create holes and features of microscopic dimensions. The level of precision achieved by machining ensures seamless integration of components onto circuit boards, significantly reducing the risk of defects and malfunctions. Moreover, these machines equipped with multi-axis capabilities further enhance the versatility and accuracy of the drilling and milling processes, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries that were previously challenging to achieve manually.
3. CNC Machining for Creating Custom Connectors and Sockets

Source: hubs.com
CNC machining is instrumental in creating custom connectors and sockets for the electronics industry. With its precision and versatility, this technology allows manufacturers to fabricate connectors with unique shapes and configurations tailored to specific device requirements. This customization ensures a perfect fit and optimal performance, enhancing the reliability of electronic devices. Rapid prototyping capabilities of machining enable engineers to swiftly iterate and validate connector designs, expediting the product development process. Whether it’s designing connectors for innovative electronic gadgets or complex industrial applications, machining empowers manufacturers to meet diverse connectivity needs efficiently and effectively.
4. Enhancing Heat Dissipation with CNC-Machined Heat Sinks
Heat dissipation is a critical concern in electronic devices, as excessive heat can lead to reduced performance and even permanent damage. CNC machining is instrumental in creating intricate heat sinks that efficiently dissipate heat and maintain the device’s temperature within safe operating limits. The ability to produce complex geometries allows for maximizing the surface area of heat sinks, thereby improving thermal performance. As electronic devices become more powerful and compact, CNC-machined heat sinks play a crucial role in their thermal management.
5. How CNC Ensures Tight Tolerances in Electronic Parts
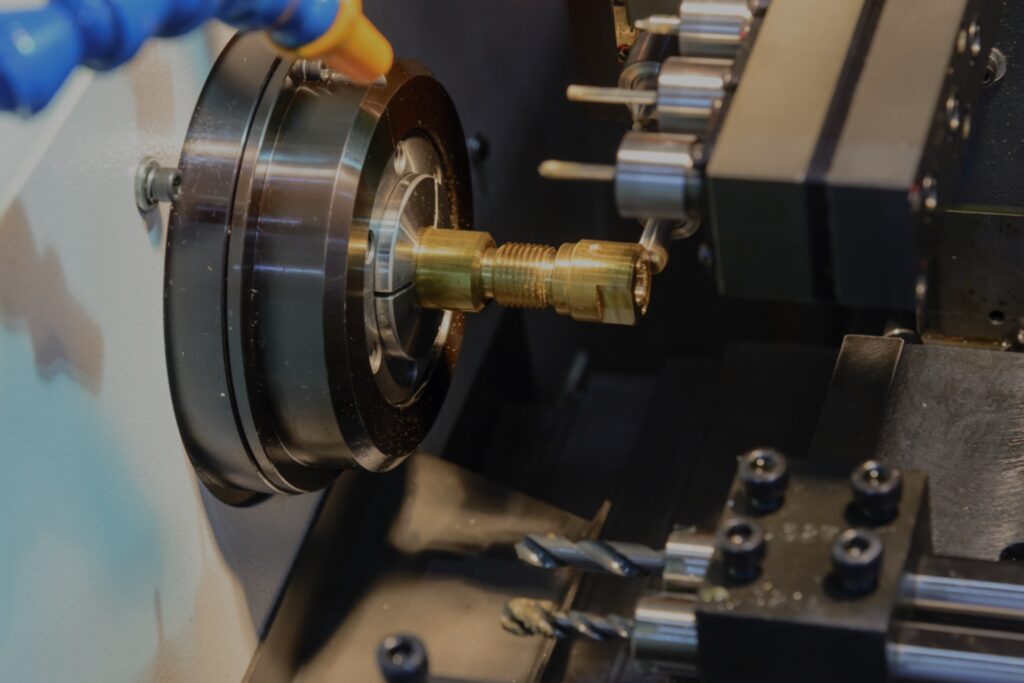
Source: fastradius.com
Tolerances, the allowable deviation from desired specifications, are of utmost importance in electronics manufacturing. Even slight variations can lead to substantial performance differences. It guarantees tight tolerances by relying on computer-controlled processes, eliminating the human error factor. This results in consistently precise electronic parts, leading to enhanced device performance and reduced rejection rates during quality control. As technology advances, the demand for increasingly tighter tolerances is met efficiently by machining.
6. CNC Automation Streamlining Electronics Production Lines
These machines are at the forefront of automation in electronics manufacturing. They can run continuously with minimal human intervention, streamlining production lines and improving overall efficiency. The integration of robotic arms further enhances automation, enabling seamless material handling and part retrieval. By reducing reliance on manual labor, automation ensures consistent quality and significantly reduces production lead times, allowing electronics manufacturers to meet market demands with greater agility.
Moreover, these advanced systems, often incorporating Texas Instruments product, elevate precision in component placement and soldering processes. This integration ensures the flawless execution of intricate tasks, previously prone to human error. Consequently, manufacturers can tackle complex electronics assembly with unprecedented speed and accuracy, solidifying their competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. The blend of reliable products available in this field and cutting-edge automation technologies marks a transformative era in electronics manufacturing, setting new benchmarks for quality and efficiency.
7. Using CNC for Rapid Prototyping of Electronic Devices
Source: cncpartsxtj.com
The electronics industry thrives on innovation, and rapid prototyping is a cornerstone of the design process. CNC machining excels in this area, enabling quick and cost-effective production of prototypes. Design iterations can be executed swiftly, allowing engineers to fine-tune electronic device designs before mass production. The ability to work with a wide range of materials also facilitates the evaluation of different concepts, ensuring that the final product meets both technical and aesthetic requirements.
8. CNC Machining for Manufacturing Antenna Arrays
Antenna arrays are integral components in various wireless communication systems, such as Wi-Fi routers, cellular networks, and radar systems. CNC machining plays a crucial role in manufacturing these arrays with precision and repeatability. The ability to create intricate patterns and structures on a variety of materials ensures optimal signal reception and transmission. As the demand for efficient wireless communication continues to grow, machining will remain essential in producing advanced antenna arrays.
9. Cost-Effectiveness of CNC in Electronic Component Fabrication
Source: cncpartsxtj.com
Though machining initially requires investment in machinery and training, it ultimately proves to be cost-effective in electronic component fabrication. The reduction in labor costs due to automation, the elimination of human error, and the optimized material usage all contribute to significant savings over time. Moreover, the ability to create intricate designs in a single setup minimizes the need for multiple manufacturing processes, further streamlining production and reducing overall costs.
10. Future Prospects of CNC Technology in the Electronics Sector
Source: rapiddirect.com
As technology advances, the electronics industry will continue to evolve, and CNC machining will play an increasingly pivotal role in this transformation. With the ongoing miniaturization of electronic components and the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, the demand for intricate and compact designs will surge. CNC machining’s versatility, precision, and automation capabilities make it ideally suited to meet these emerging challenges, driving innovation and progress in the electronics sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CNC machining has revolutionized the electronics industry, influencing every aspect of manufacturing, from circuit board designs to antenna arrays. Its role in producing precise components, enabling automation, and streamlining production lines is indispensable. As technology progresses, CNC machining will continue to shape the electronics landscape, making our electronic devices more efficient, powerful, and compact than ever before. With its vast potential for innovation, the future of CNC technology in the electronics sector is boundless.







