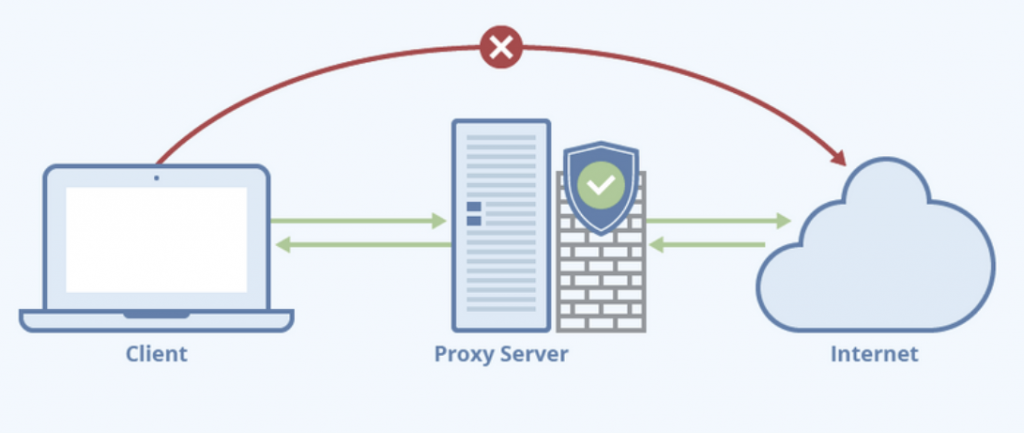
A proxy server can be anything from a piece of code that runs on your computer to a hardware appliance on a datacenter. It can be shared, dedicated, private, public, or based on a specific protocol. Classifying proxies into different types and categories can be quite challenging, as their characteristics may vary greatly.
For example, a proxy can be a top anonymity proxy or a simple forwarding device. If you are connected to the Internet while reading this, then you are probably behind some type of tunneling proxy (your Internet Gateway).
In this post, we’ll discuss the most common types of proxies. We’ll classify them on different types and provide a brief description of each.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents.

img source: optimum7.com
Based on Location:
- Tunneling Proxy.
- Forwarding Proxy.
- Reverse Proxy.
Based on Level of Anonymity.
- Transparent Proxy (Level 3).
- Anonymous Proxy (Level 2).
- Elite or High-Anonymity Proxy (Level 1).
Based on Protocol and Application.
- SOCKS Proxy Server.
- FTP Proxy Server.
- The DNS Proxy
- Smart DNS Proxy.
- HTTP Proxy Server.
- SSL Proxy or HTTPS Proxy Server.
- TOR Onion Proxy.
- CGI Proxy.
Based on Services.
- Distorting Proxy.
- Residential Proxy.
- Rotating Residential Proxies.
- Data Center Proxy.
- Public Proxy.
- Private Proxy.
- Dedicated Proxy.
- Shared Proxy.
1. Based on Location.
- Tunneling Proxy: The proxy that forwards requests and responses without modifying them is known as a tunneling proxy. The most common tunneling proxy is your Internet Gateway.
- Forwarding Proxy: The forwarding proxy is the most popular type of proxy facing the Internet. It acts on behalf of requesting hosts (or clients) in order to hide their true identities. These proxies are used to retrieve data from sources on the Internet.
- Reverse Proxy: This type of proxy does the opposite of a forwarding proxy. It is also an Internet-facing proxy but it used to protect and control traffic coming from the Internet to an internal server. If a forwarding proxy hides the identity of a user, reverse proxies hide the identity of servers. The reverse proxy is also used for tasks like authentication, decryption, load-balancing, compression, and caching.
2. Based on Level of Anonymity.
- Transparent Proxy (Level 3). A type of forwarding proxy, usually located between the client and server (Internet). They are also known as intercepting proxy, inline proxy, or forced proxy. Transparent proxies advertise themselves as proxy servers and reveal the original IP address— they do not modify the request/response. These are often used for faster website retrieval with caching and compressing.
- Anonymous Proxy (Level 2). These types of proxies are the most popular forwarding proxy— they are commonly referred to as the web proxy server. These proxies advertise themselves as proxies but DO NOT reveal the source IP. These proxy servers hide the original IP address, so they are very useful for anonymous web browsing.
- Elite or High-Anonymity Proxy (Level 1). These servers leave no trace of being a proxy and they look like the normal requesting client. They are the highest level of anonymity because first they don’t advertise themselves as proxies and hide the originating IP.
3. Based on Protocol and Application.
- SOCKS Proxy Server. SOCKS stands for Sockets Secure, and is a network protocol that simplifies communication with servers through a firewall. The SOCKS protocol routes packets between server and client through the proxy server. The SOCKS5 proxy is the latest version. It has improved security and different types of authentication.
- FTP Proxy Server. Serves as a relay for the FTP protocol communications. It can be used to control FTP connections based on source and destination addresses or authentication. It can also be used to limit transfers and file shares.
- The DNS Proxy. This type of proxy takes the DNS queries and forwards them to a specific DNS server. The DNS proxy is useful for improving domain lookup performance by caching DNS records.
- The Smart DNS Proxy. Smart DNS proxies take your request and re-route it to a dedicated proxy located in the country where you are trying to access specific content. Smart DNS proxies are often used to access geo-restricted content, such as Netflix, Hulu, HBO, etc.
- HTTP Proxy Server. A reverse proxy that operates between the web server and the client. This proxy processes and analyzes the HTTP traffic before sending it to an internal webserver/client. It helps identify suspicious HTTP traffic that may lead to an attack. HTTP proxies are used to protect web servers.
- SSL Proxy or HTTPS Proxy Server. The SSL proxy guarantees SSL encryption in every request or response packet. The SSL proxy provides similar security as connecting to a normal SSL-certified website. With this type of server, your HTTP traffic cannot be intercepted.
- TOR Onion Proxy. TOR (The Onion Router) uses a system of worldwide volunteer servers to relay and encrypt traffic and provide a high level of anonymity. TOR makes Internet-tracing very difficult. A TOR Onion Proxy is used to increase the level of anonymity by making the other end of the connection unaware of TOR. If the endpoint is blocking TOR or if it could be capable of identifying TOR, then a TOR Onion Proxy can be useful.
- CGI Proxy. A Common Gateway Interface (CGI) proxy looks like a normal website but it allows a user to anonymously access a different site through it. The CGI proxy usually works through an encrypted web form embedded on another website using SSL. These types of proxies are used via the web browser.
img source: medium.com
4. Based on Services.
- Distorting Proxy. A type of anonymous proxy that identifies itself as a proxy but purposefully passes along a false IP address in all requests. This can be helpful when trying to appear somewhere else, as a distorting proxy can provide an IP address from a specific location. Similar to the purpose of a Smart DNS proxy.
Residential Proxy. These types of proxies are very popular because they look like a normal real-time client requesting a service. They use a real IP address from a real physical device. Residential proxies get that name because they get their IP address from ISPs or other Local Internet Registries (LIRs)— not a data center. These proxies get their own browser information, cookies, and normal geo-location. Residential Proxies like geonode.com do not charge for bandwidth. They always provide you residential proxies without mixing in data center proxies. You’ll get faster and more predictable results every time. - Rotating Residential Proxies. Also known as back connect proxies, rotating residential proxies hide the identity of the source behind a pool of IP addresses. Rotating proxies switch to a brand new IP for every new session or at a specific interval. Rotating proxies are frequently used for web scraping.
- Data Center Proxy. These are computer-generated IP addresses and are not affiliated to a particular ISP or LIR. Datacenter proxies aren’t attached to a real device that looks like real people as residential proxies do. These types of proxies are preferred for their speed but unfortunately, they can be easily flagged.
- Public Proxy. Public proxies are also referred to as open proxies. They are free forwarding proxies used by many people at the same time. Public proxies are insecure, unreliable, and slow, but they are free, so a lot of people use them a lot. Public proxies are found easily via free proxy lists but there are hardly reliable ones.
- Private Proxy. Provided by a proxy service provider with a price. Private proxies are far more reliable, fast, and secure than free public ones. Companies such as Rapidseedbox that supply IPv6 rotating proxies can provide entire pools of IPs that aren’t crowded with noisy neighbors as public proxies are.
- Dedicated Proxy. These types of proxies are always private. They are offered via high-end servers with dedicated resources like network bandwidth. These proxies solve the problem of “noisy neighbors” by allowing only one client to connect and send requests.
- Shared Proxy. These proxies are also private proxies. They are cheaper than dedicated proxies, because, as the name implies, the resources are shared with other users. Shared proxies usually handle many requests and responses at the same time, so they are usually very slow.
Final Words.

img source: netlify.app
With proxies, there is no one-size-fits-all type-of solution, as the “type” would really vary according to your resources and demands. For example, anonymous proxies are very popular but they vary according to what you are looking for. There could be free public anonymous proxies, private dedicated anonymous proxies, and the list goes on.
Types of proxies may vary from location, level of anonymity, protocol/application, and services. Although there could be more types of proxies as described in this article, we covered the most popular and frequently used.
We hope you found the article informative and useful!