
In an era marked by technological advancement, facial recognition technology stands out as a significant innovation with wide-ranging applications. Central to the accessibility and usability of this technology are Face Recognition APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of Facial Recognition API, exploring what they are, how they work, their applications, ethical considerations, and finally, a comparative analysis of some leading Face Recognition APIs in the market.
Table of Contents
Understanding Face Recognition APIs
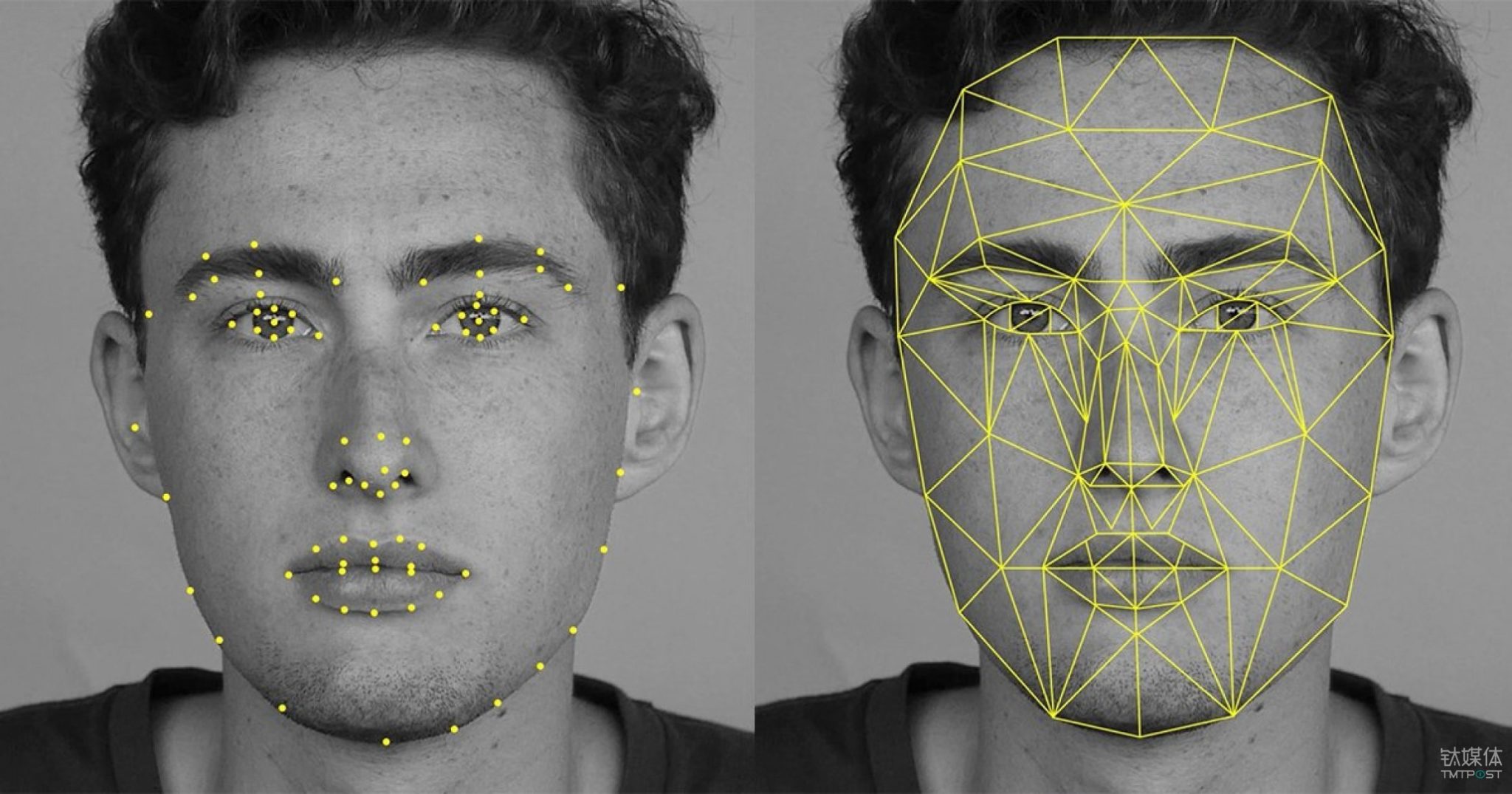
Source: rapidapi.com
At its core, a Face Recognition API serves as a bridge between developers and the complex algorithms required to perform facial recognition tasks. It provides developers with pre-built functionalities and tools to integrate facial recognition capabilities seamlessly into their applications, without the need to develop the algorithms from scratch.
Key Components of Face Recognition APIs
- Face Detection: The API identifies and locates human faces within images or video streams. This involves analyzing pixel data to detect facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Face Verification: This process involves comparing a detected face against a known database to verify the identity of an individual.
- Face Identification: Unlike verification, identification involves matching a detected face against a database of multiple faces to determine the most likely match.
- Facial Attribute Analysis: Many APIs offer additional features such as age estimation, gender recognition, emotion detection, and facial landmark detection.
How Face Recognition APIs Work

Source: edenai.co
Face Recognition APIs utilize sophisticated algorithms, often based on deep learning and computer vision techniques, to analyze and process facial data.
These algorithms typically follow a series of steps:
- Preprocessing: The input image is preprocessed to enhance features and remove noise.
- Feature Extraction: Key facial features, such as eyes, nose, and mouth, are extracted from the preprocessed image.
- Encoding: The extracted features are converted into a mathematical representation known as a face embedding or feature vector.
- Matching: The face embeddings are compared against a database of known faces to determine a match or similarity score.
Applications of Face Recognition APIs:
- Facial recognition is used in security systems for access control, surveillance, and identity verification.
- It is employed in various applications, including unlocking smartphones, accessing secure facilities, and online identity verification.
- Facial recognition enables personalized experiences in applications such as social media, e-commerce, and entertainment.
- Law enforcement agencies use facial recognition for suspect identification, missing person searches, and forensic analysis.
- Facial recognition technology has applications in healthcare for patient identification, monitoring, and analysis.
Ethical Considerations:
While facial recognition technology offers numerous benefits, it also raises significant ethical concerns, including privacy, surveillance, bias, and consent. There are concerns about the potential misuse of facial recognition technology, including mass surveillance, unauthorized tracking, and discrimination.
Comparative Analysis of Leading Face Recognition APIs:
- Banuba Face Recognition API: Banuba’s Face Recognition API offers real-time face tracking, detection, and recognition optimized for mobile platforms, with comprehensive facial attribute analysis.
- Amazon Rekognition: Developed by Amazon Web Services, Rekognition offers robust facial analysis and recognition capabilities with high accuracy and scalability.
- Microsoft Azure Face API: Azure Face API provides powerful facial recognition features, including face detection, verification, identification, and facial attribute analysis.
- Google Cloud Vision API: Google’s Cloud Vision API offers accurate face detection and recognition capabilities, leveraging machine learning models trained on vast datasets.
Conclusion
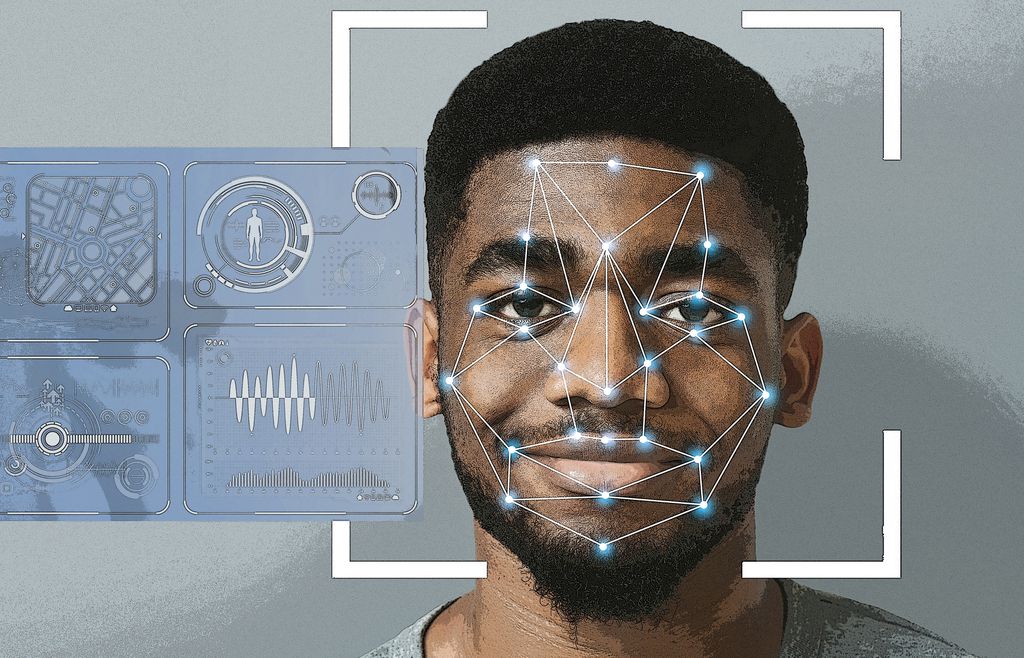
Source: thestartupfounder.com
Industries that rely on facial recognition software, such as security, retail, and healthcare, benefit immensely from the advanced functionalities provided by Face Recognition APIs, enhancing efficiency and security measures.
While offering numerous benefits, they also pose significant ethical challenges that must be addressed. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the implications of facial recognition and ensure responsible development and deployment practices.
With a diverse range of Face Recognition APIs available, developers have the opportunity to create innovative and impactful applications while upholding ethical standards and protecting user privacy.







